How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from capturing breathtaking aerial photography to exploring the intricacies of advanced flight controls. Mastering drone operation requires a blend of technical understanding, safety awareness, and practical skill. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take flight responsibly and capture stunning visuals.
From pre-flight checks and understanding regulations to mastering the controls and post-flight data management, we’ll cover every aspect of safe and effective drone operation. We’ll delve into the nuances of camera settings, battery management, and troubleshooting common issues, ensuring you’re prepared for any situation. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive guide provides a clear path to becoming a proficient drone pilot.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone’s components, understanding local regulations, and preparing for potential emergencies. Failing to do so can lead to accidents, damage, and legal repercussions.
Drone Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection ensures the drone is in optimal condition. This systematic check helps prevent malfunctions and potential accidents during flight.
| Item | Check | Action Required | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for damage, cracks, or looseness. | Replace damaged propellers. Tighten loose propellers. | Ensure all propellers are securely attached. |
| Battery | Check battery level and condition. | Charge battery if necessary. Replace damaged batteries. | Note the battery’s remaining flight time. |
| Gimbal | Verify gimbal movement and stability. | Adjust or calibrate gimbal if needed. | Ensure smooth and accurate camera movement. |
| Camera | Check camera lens for smudges or obstructions. | Clean lens gently. | Ensure clear and unobstructed camera view. |
| Sensors | Inspect all sensors (GPS, IMU, etc.) for damage or obstructions. | Clean sensors gently if needed. | Ensure sensors are functioning correctly. |
| Radio Connection | Test the connection between the drone and the remote controller. | Restart both devices if connection is weak. | Maintain a strong signal throughout the flight. |
Local Regulations and Airspace Restrictions

Understanding and adhering to local drone regulations and airspace restrictions is paramount. Ignorance of these rules can result in hefty fines, legal action, and even criminal charges.
For example, flying near airports or restricted areas without proper authorization is strictly prohibited. Similarly, flying beyond visual line of sight (BVLOS) without the necessary permits is illegal in most jurisdictions. Consequences can range from warnings and fines to equipment confiscation and imprisonment, depending on the severity of the violation.
Emergency Procedures
Preparation for potential emergencies is crucial for safe drone operation. Knowing how to react in various situations can minimize damage and ensure personal safety.
- Loss of Signal: Immediately initiate Return-to-Home (RTH) function if available. If RTH fails, attempt to manually guide the drone back to the pilot, prioritizing safety.
- Battery Failure: Initiate RTH immediately if possible. If not, prioritize a controlled landing in a safe location.
- Unexpected Weather: Land the drone immediately in a safe location. Avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or snow.
Safe Operating Practices, How to operate a drone
Safe operating practices minimize the risk of collisions and accidents. Maintaining awareness of surroundings is key to preventing incidents.
- Always maintain visual line of sight (VLOS) with the drone.
- Avoid flying near people or animals.
- Be aware of obstacles such as trees, buildings, and power lines.
- Fly in open areas whenever possible.
- Never fly under the influence of drugs or alcohol.
Drone Controls and Navigation: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding your drone’s controls and navigation is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section provides a step-by-step guide to getting started and mastering your drone’s flight capabilities.
Powering On and Calibrating
- Power on the remote controller.
- Power on the drone.
- Wait for the GPS signal to lock (if applicable).
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) according to the drone’s manual instructions. This typically involves rotating the drone slowly in a circular motion.
- Check for any pre-flight warnings or error messages on the remote controller display.
Remote Controller Controls
The remote controller is the primary interface for controlling your drone. Understanding each control is vital for safe and precise maneuvers.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. A crucial aspect is learning the intricacies of controlling the drone itself, and for comprehensive guidance on this, I recommend checking out this helpful resource: how to operate a drone. Proper training ensures safe and effective drone operation, ultimately leading to a rewarding flying experience.
| Control | Function | Typical Response |
|---|---|---|
| Left Stick (Vertical/Horizontal) | Controls altitude and yaw (rotation around the vertical axis). | Pushing the stick up increases altitude; pushing it down decreases altitude. Moving the stick left or right rotates the drone left or right. |
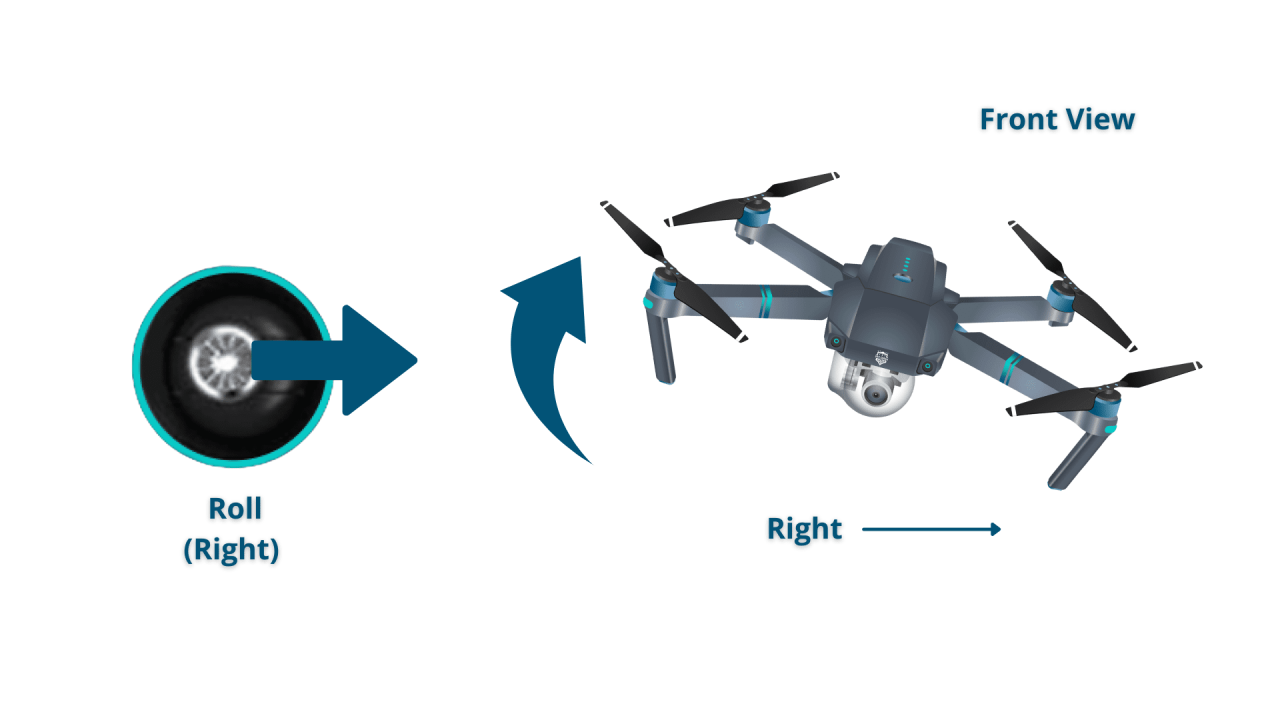
| Right Stick (Vertical/Horizontal) | Controls pitch (forward/backward tilt) and roll (left/right tilt). | Pushing the stick forward moves the drone forward; pushing it backward moves it backward. Moving the stick left or right tilts the drone left or right. |
| Buttons/Switches | These vary by drone model, but typically include functions like Return-to-Home (RTH), camera control, and flight mode selection. | Refer to your drone’s user manual for specific functions and responses. |
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability, catering to different skill levels and flight scenarios.
- Beginner Mode: Limits speed and responsiveness, ideal for learning and practicing basic maneuvers. Provides stability and prevents aggressive movements.
- Sport Mode: Increases speed and responsiveness, allowing for more dynamic and agile flight. Requires more skill and precision.
- GPS Mode: Utilizes GPS for precise positioning and stability, enabling features like Return-to-Home (RTH) and waypoint navigation. Offers more stable hovering and less sensitivity to wind.
Drone Navigation
Mastering basic maneuvers like takeoff, landing, hovering, and directional movement is crucial for effective drone control.
- Takeoff: Gently push the left stick upwards to initiate a smooth ascent.
- Landing: Gently push the left stick downwards to initiate a controlled descent.
- Hovering: Maintain a steady position in the air by keeping the left stick centered.
- Directional Movement: Use the right stick to control pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right) movements.
Camera Operation and Image Capture
The drone’s camera capabilities are a key feature, allowing for stunning aerial photography and videography. Understanding camera settings and techniques will greatly enhance the quality of your captures.
Camera Settings Adjustment
Adjusting camera settings allows for fine-tuning image quality to suit different lighting conditions and creative goals.
| Setting | Effect on Image Quality |
|---|---|
| Resolution | Higher resolution results in larger, more detailed images, but requires more storage space. |
| ISO | Higher ISO values allow for shooting in low-light conditions but can introduce noise (grain) into the image. |
| Shutter Speed | Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower shutter speeds can create motion blur. |
| Aperture | Wider apertures (lower f-stop numbers) allow for more light to enter the camera, creating a shallow depth of field (blurred background). Narrower apertures (higher f-stop numbers) increase depth of field (more in focus). |
Photo and Video Capture
Capturing photos and videos involves using the dedicated buttons or controls on the remote controller.
- Position the drone for the desired shot.
- Adjust camera settings as needed.
- Use the designated button or control to take photos or start/stop video recording.
Camera Angles and Perspectives
The ability to achieve various camera angles and perspectives is a significant advantage of drone photography.
- High-angle shots provide a wide overview of a scene.
- Low-angle shots emphasize scale and grandeur.
- Dutch angles create a dynamic and unsettling effect.
- Tracking shots follow a subject in motion.
Professional Aerial Video Capture
Creating professional-looking aerial videos involves careful planning, execution, and post-processing.
- Planning: Storyboard the shot, considering the desired angles, movements, and overall narrative.
- Execution: Fly smoothly and precisely, maintaining a steady camera movement.
- Editing: Use video editing software to refine the footage, adding music, sound effects, and transitions.
Battery Management and Maintenance
Proper battery management and maintenance are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone’s batteries and ensuring safe operation. Neglecting these aspects can lead to premature battery failure and potential safety hazards.
Charging and Storage
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for charging and storing your drone batteries. This typically involves using the provided charger and storing batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
- Always use the manufacturer-recommended charger.
- Avoid overcharging or discharging batteries.
- Store batteries at a moderate temperature.
Signs of Battery Failure
Recognizing signs of a failing battery is essential for preventing unexpected power loss during flight. Common signs include reduced flight time, slower charging, and unusual swelling or deformation of the battery.
- Reduced flight time compared to previous flights.
- Slower charging times.
- Physical damage or swelling of the battery.
- Unusual heat generation during charging or operation.
Battery Flight Time and Cycle Records

Keeping accurate records of battery flight times and cycles helps monitor battery health and predict potential issues. This information is valuable for planning flights and replacing batteries as needed.
Use a spreadsheet or app to log each flight, noting the date, duration, and battery used. Track the number of charge cycles for each battery.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, such as taking off and landing smoothly, is crucial, and mastering more advanced maneuvers takes practice. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced flight techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone.
This will help ensure safe and efficient drone operation.
Routine Maintenance
Regular maintenance ensures your drone operates optimally and extends its lifespan. A schedule of routine checks will prevent more serious issues.
- Inspect propellers for damage before each flight.
- Clean the drone body and sensors regularly.
- Check for loose screws or connections.
- Inspect the gimbal for smooth movement.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU periodically.
- Store the drone in a clean, dry place when not in use.
Post-Flight Procedures and Data Management
Proper post-flight procedures and data management are essential for preserving your drone footage and ensuring the safety of your equipment. This section details the necessary steps to ensure your data is safely stored and easily accessible.
Landing and Powering Down
Safe landing and powering down procedures minimize the risk of damage to the drone and its components. Always ensure a stable landing surface is available before initiating a descent.
- Select a suitable landing area.
- Initiate a controlled descent using the left stick.
- Power down the drone after landing.
- Power down the remote controller.
Downloading and Managing Photos and Videos
Efficiently downloading and managing your drone footage ensures you have easy access to your work. Various methods exist for transferring data, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Use a memory card reader to transfer files to a computer.
- Connect the drone directly to a computer via USB.
- Use a wireless connection to transfer files to a smartphone or tablet.
Organizing and Backing Up Drone Data
Organizing and backing up your drone data protects against loss and ensures long-term accessibility. Consider cloud storage solutions or external hard drives to maintain multiple copies of your valuable footage.
- Create a structured folder system to organize your drone footage by date, location, or project.
- Regularly back up your drone footage to multiple locations.
- Consider using cloud storage services for off-site backups.
Software and Applications for Processing and Editing
Numerous software applications are available for processing and editing drone footage, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right software depends on your specific needs and budget.
- Adobe Premiere Pro
- DaVinci Resolve
- Final Cut Pro
- HitFilm Express
Successfully operating a drone involves more than just understanding the controls; it demands a commitment to safety, responsible operation, and continuous learning. By following the guidelines Artikeld in this guide, you can confidently navigate the skies, capture incredible footage, and explore the limitless potential of aerial technology. Remember to always prioritize safety, respect regulations, and continue to expand your knowledge to become a responsible and skilled drone pilot.
Key Questions Answered
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are available for beginners, often featuring GPS stabilization and automated flight modes. Look for models with intuitive controls and safety features.
How often should I calibrate my drone?
Calibration is usually needed before the first flight and after any significant impact or if the drone behaves erratically. Check your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
What should I do if my drone loses signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If signal is lost, the drone will automatically attempt to return to its takeoff point. However, always keep a visual on your drone during flight.
How do I obtain necessary permits or licenses for drone operation?
Regulations vary by location. Check with your local aviation authority to understand and comply with all applicable laws and regulations before flying.
